Unleashing the Power of the Rotary Engine
Revolutions go beyond just political and economic change; they also come in the form of technological advances. For car enthusiasts, few inventions hold as much fascination as the rotary engine – an innovative engineering marvel with a captivating history that has enabled drivers to experience new levels of speed, power, and performance on the open roads.
With its extraordinary efficiency and remarkable torque characteristics, this engine type has gained significant attention over recent years for its ability to take vehicles to higher heights than ever before.
In today’s blog post, we will be delving into the inner workings of these engines and exploring how owners can unlock their true potential on the track or road – all while keeping your vehicle running at peak condition for miles upon miles!

Exploring the Rotary Engine Design
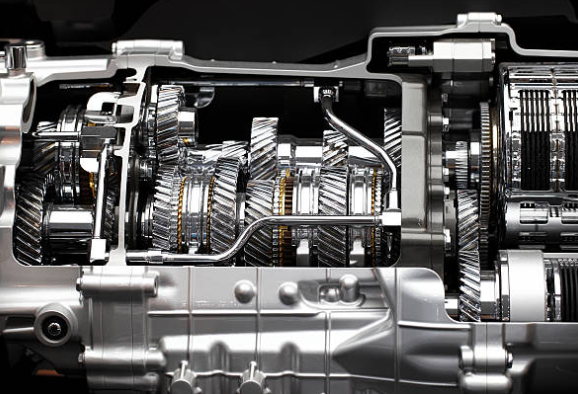
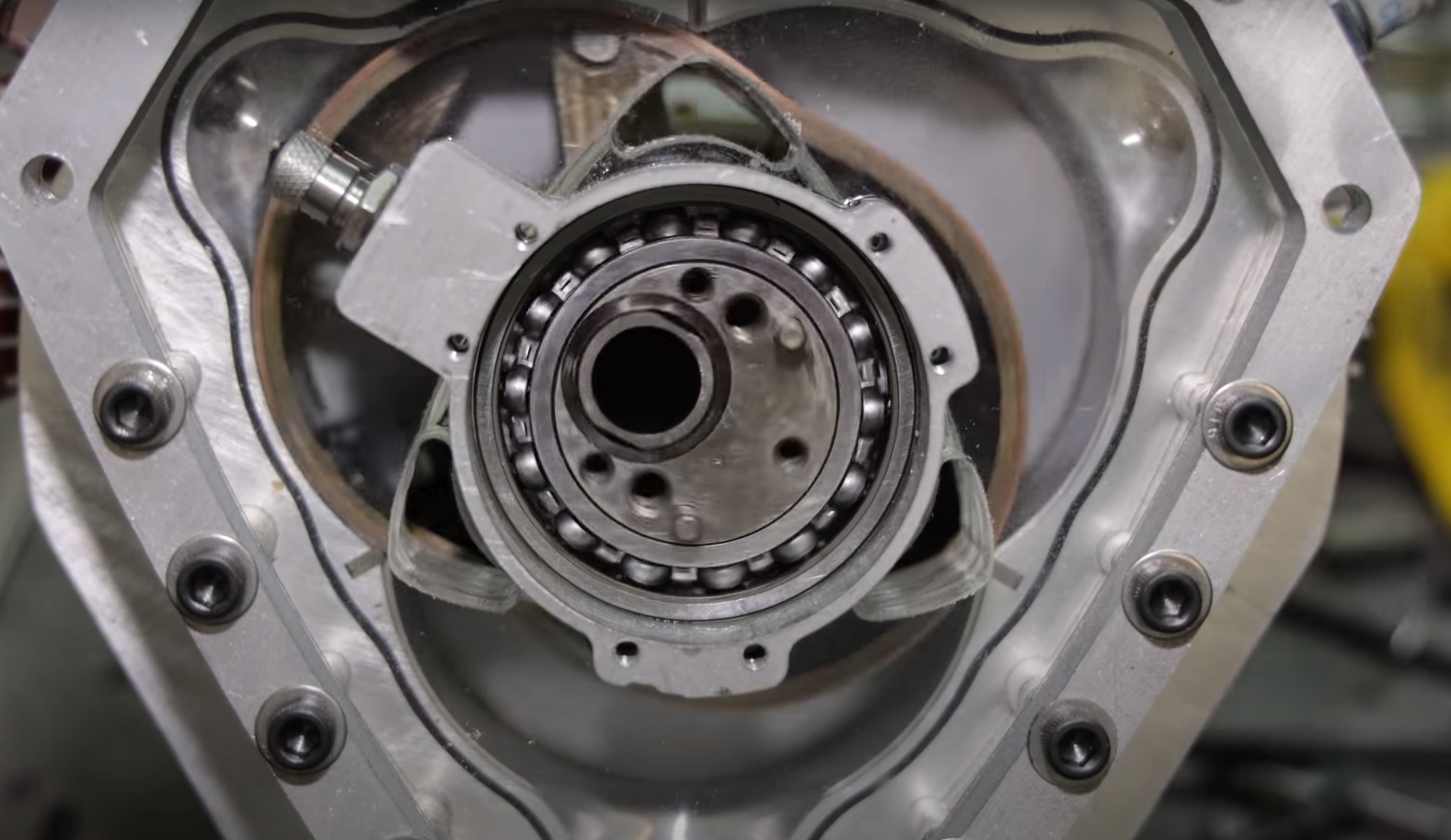
The rotary engine, also known as the Wankel engine, stands out as a distinct and intriguing departure from conventional piston engines. Developed by Felix Wankel in the 1950s, this innovative powerplant operates on a unique rotary motion, featuring a triangular rotor spinning within an epitrochoidal housing.
Its compact and lightweight design, coupled with the ability to reach high RPMs, makes it popular in certain niche markets, particularly in high-performance sports cars and aircraft. The rev-happy nature of the rotary engine contributes to a thrilling driving experience, accompanied by a signature engine sound.
Despite these advantages, challenges remain, such as fuel efficiency, emissions, and apex seal wear. While the rotary engine has not achieved widespread use in mainstream automobiles, ongoing research and development may hold the potential for its resurgence in the future. The legacy of the rotary engine as a symbol of engineering ingenuity and innovation continues to captivate automotive enthusiasts worldwide.
Design and Operation:
- Rotary Engine: Operates on a rotating motion of a triangular rotor within an epitrochoidal housing. This results in continuous combustion chambers, providing a simple design with fewer moving parts.
- Piston Engine: Uses reciprocating motion of pistons within cylindrical cylinders. The motion is translated into rotating motion via a crankshaft, making it a more complex design with additional moving parts.
Size and Weight:
- Rotary Engine: Generally more compact and lighter due to its simpler design, making it suitable for applications with space and weight constraints.
- Piston Engine: Typically larger and heavier due to the need for additional components, making it more suitable for larger vehicles.
Revving Capabilities:
- Rotary Engine: Excels in high RPM capabilities, offering a rev-happy nature that is ideal for quick acceleration and sports cars.
- Piston Engine: Can reach high RPMs, but may not match the rotary engine's quick revving capabilities. Piston engines are more commonly used across a wider range of vehicle types and applications.
Smoothness and Vibrations:
- Rotary Engine: Known for its smoother operation and reduced vibrations due to the balanced rotary motion.
- Piston Engine: May produce more vibrations due to the reciprocating motion of pistons.
Fuel Efficiency and Emissions:
- Rotary Engine: Historically struggled with fuel efficiency and emissions due to its unique design and combustion characteristics.
- Piston Engine: Can achieve better fuel efficiency and meet stringent emissions standards, especially with advancements in technology.
Maintenance and Durability:
- Rotary Engine: Requires specific maintenance, particularly concerning apex seals, which can wear over time and affect engine performance.
- Piston Engine: Generally known for its durability and longevity, with a more established maintenance and repair infrastructure.
Sound and Driving Experience:
- Rotary Engine: Offers a distinctive engine sound and a thrilling driving experience, especially at high RPMs.
- Piston Engine: Provides a variety of sounds depending on engine configuration, offering a more traditional engine sound.
Applications:
- Rotary Engine: Historically found success in certain niche markets, such as sports cars, motorcycles, and some aviation applications.
- Piston Engine: Dominates the automotive industry and is widely used in various vehicles, including cars, trucks, buses, and industrial equipment.

Compact and Lightweight: Compared to piston engines, rotary engines feature a simpler design with fewer moving components, making them smaller and lighter. For applications where weight and space restrictions are crucial, such as in sports automobiles, motorbikes, and some airplanes, this trait is very helpful.
Smooth Operation: Rotary engines operate on a balanced rotary motion, resulting in smoother engine operation with reduced vibrations compared to some piston engines. This attribute enhances the overall driving experience, particularly in high-revving performance cars.
Rev-Happy Performance: Rotary engines are renowned for their ability to rev quickly and smoothly. They can reach high RPMs effortlessly, providing immediate and responsive acceleration, which is appealing for sports car enthusiasts and performance drivers.
Distinctive Engine Sound: The unique design and firing pattern of rotary engines produce a distinctive engine sound that sets them apart from traditional piston engines. Many enthusiasts appreciate the captivating sound that rotary engines produce during high-revving operation.
Less Complex Construction: The rotary engine's design requires fewer parts compared to piston engines, resulting in potentially lower manufacturing and maintenance costs. The simplicity of the rotary engine also simplifies assembly and repair processes.
Fewer Vibration Issues: The absence of reciprocating parts, such as pistons and connecting rods, reduces vibration-related wear and tear, contributing to improved engine longevity and reduced maintenance requirements.
Adaptability in Niche Markets: Rotary engines have found success in niche markets, particularly in high-performance sports cars, racing vehicles, motorcycles, and certain aviation applications. In these specialized fields, the unique characteristics of rotary engines provide advantages that suit specific requirements.
Unique Design and Innovation: Rotary engines are considered innovative and represent an alternative to conventional engine designs. Their development has spurred engineering curiosity and exploration, leading to continuous advancements in rotary engine technology.
-
How do rotary engines sound compared to piston engines?
Rotary engines produce a distinct engine sound characterized by a high-pitched and rev-happy nature. This sound is different from the traditional engine noise of piston engines, and many enthusiasts appreciate the unique auditory experience offered by rotary engines.
-
Can I retrofit a rotary engine into my car?
Retrofitting a rotary engine into a car designed for a piston engine can be a complex and challenging task. It often requires significant modifications to the car's structure, engine mounts, and drivetrain to accommodate the different engine design and operating principles.
View another article: The 10 Best Diecast Cars