What Is Turbo Lag? And How Do You Address It?
Delve into the concept of turbo lag, grasp its intricacies, and explore strategies to effectively mitigate its impact on your driving experience.

When you shop through retailer links on our site, we may earn affiliate commissions. Learn more
"Turbo lag," a term often heard in automotive circles, refers to the delay experienced between pressing the accelerator pedal and feeling a significant surge of power in turbocharged vehicles. As turbocharging technology continues to evolve, understanding turbolag becomes increasingly crucial for both enthusiasts and everyday drivers. This phenomenon, influenced by various factors such as engine design, turbo size, and exhaust flow, significantly impacts the driving experience and plays a pivotal role in the performance characteristics of turbocharged engines.
In this exploration, we delve into the intricacies of turbo lag, unraveling its causes and effects and how advancements in automotive engineering strive to mitigate its presence in modern vehicles.
IN THIS ARTICLE
What Exactly Is Turbo Lag?How Do Turbos Work?
What Contributes To Turbo Lag?
How To Address Turbo Lag?
FAQs
Final Thoughts
What Exactly Is Turbo Lag?
Turbo lag refers to the interval between depressing the accelerator pedal and the delivery of increased air pressure to the engine. This delay occurs because the turbocharger requires time to reach the necessary speed and generate the additional air pressure that enhances engine performance.
The turbocharger's operation hinges on the energy derived from exhaust gases, which spin the turbine. Consequently, there's a brief duration before these gases generate adequate energy to propel the vehicle swiftly.
The extent of turbolag varies across different turbocharger designs. Modern iterations often feature reduced lag, owing to advancements in technology and more intricate designs. Conversely, older turbocharger models tend to exhibit prolonged delays due to their simpler construction and technological constraints.
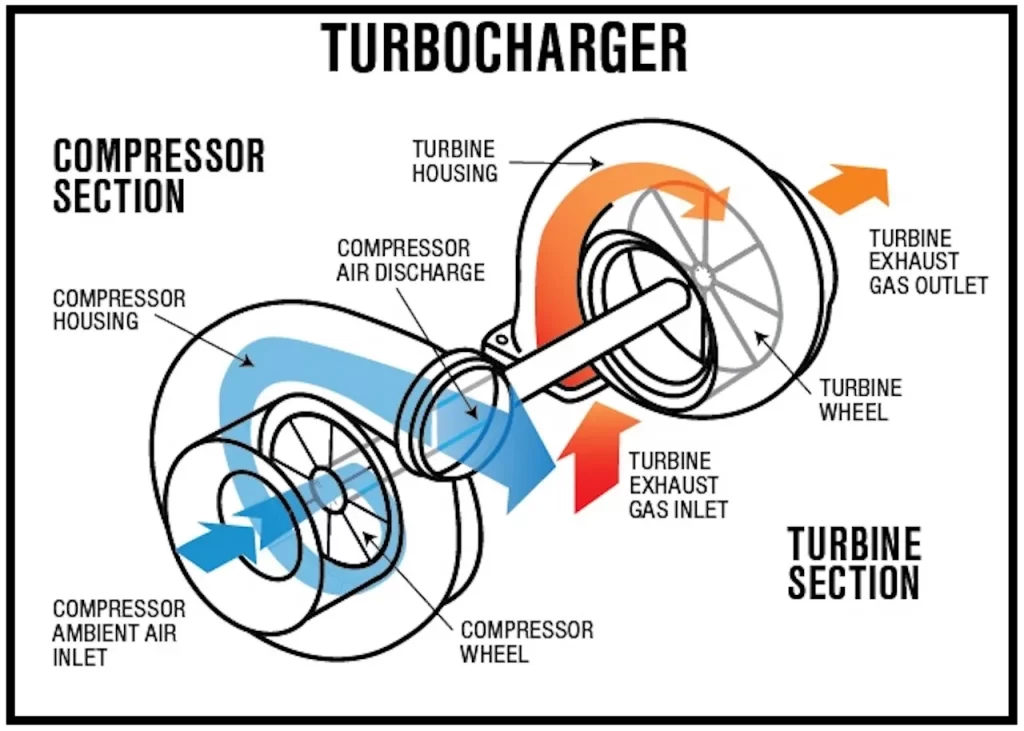
Turbochargers operate by harnessing exhaust gases produced by the engine to power a turbine, which in turn drives a compressor. This compressor then forces more air into the engine's intake manifold, increasing the volume of air available for combustion. The additional air allows for more fuel to be burned, resulting in increased power output from the engine.
Related Articles
How Do Turbos Work?
Here's a more detailed breakdown of how turbos work:
- Exhaust Gas Flow: As the engine burns fuel, it produces exhaust gases that exit through the exhaust manifold.
- Turbine: The exhaust gases flow through the turbine housing, where they spin a turbine wheel. This turbine is connected to a shaft that rotates at high speeds.
- Compressor: On the same shaft as the turbine, there is a compressor wheel located in the compressor housing. As the turbine spins, it also spins the compressor wheel.
- Air Compression: The spinning compressor wheel draws in ambient air and compresses it before delivering it into the engine's intake manifold. This compressed air is at a higher pressure than atmospheric pressure, which increases the engine's power output.
- Intercooler (optional): In some turbocharged systems, an intercooler is used to cool the compressed air before it enters the engine. Cooler air is denser, resulting in even greater power gains.
Overall, turbochargers effectively increase engine power by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, allowing for more efficient combustion and greater performance.
What Contributes To Turbo Lag?
The engine operates as a complex interplay of various components, each contributing to its functioning. Turbochargers, integrating into this system, utilize waste energy to perform their tasks, making them reliant on the seamless operation of all components for optimal functionality and efficiency.
Several factors influence the extent of turbolag:
- Time required for exhaust gases to accumulate energy.
- Inertia of turbine and compressor components.
- Delays in delivering the air-fuel mixture.
- Design considerations.
- Engine size.
While larger turbochargers can produce a more substantial boost, they necessitate more time to accumulate the requisite volume of exhaust gases to spin the turbine. Consequently, a larger turbo does not necessarily translate to reduced lag.
Conversely, smaller turbos typically exhibit less lag due to their lower inertia and the reduced volume of exhaust gas needed to reach their optimal rotational speed.
In summary, it's imperative to acknowledge that turbolag remains a consideration irrespective of the type of turbocharger employed.

How To Address Turbo Lag?
When turbo lag becomes excessively long, it can significantly impact the driving experience, leading to frustration for the driver. Particularly in heavy-duty vehicles reliant on prompt power delivery for tasks like towing, an extended lag can impede performance and lead to operational failures.
In such scenarios, one potential solution is to install a new turbocharger, though this option is often costly. Over time, it may become evident that an outdated or worn turbocharger is unable to meet the demand for an increased boost.
If turbo lag stems from a malfunction, prompt inspection of the vehicle is advisable. Symptoms of a faulty turbocharger, which may accompany prolonged lag, include:
- Excessive smoke emissions
- Unusual noises from the engine
- Oil leaks in the engine bay
- Inconsistent boost pressure
- Elevated exhaust gas temperature
- Detection of a burnt oil odor emanating from the exhaust system.
FAQs
How does turbo lag affect driving?
Turbo lag can lead to delayed throttle response and a perceived lack of power at lower engine speeds, impacting the driving experience, particularly during sudden acceleration or overtaking maneuvers.
Can turbolag be reduced or eliminated?
While it's challenging to eliminate turbolag entirely, various engineering solutions and technological advancements aim to minimize its effects. These include variable-geometry turbos, twin-scroll turbochargers, electronic wastegates, and optimized engine tuning.
Is turbolag present in all turbocharged vehicles?
Turbo lag varies depending on factors such as turbocharger design, engine size, and vehicle application. While some modern turbocharged engines exhibit minimal lag, older or high-performance vehicles may experience more pronounced delays in power delivery.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, turbolag is a fascinating aspect of turbocharged engine performance that impacts both enthusiasts and everyday drivers. Understanding its causes and effects, as well as potential solutions to mitigate its impact, empowers drivers to enhance their driving experience. Whether navigating city streets or tackling challenging terrain, a deeper understanding of turbolag unlocks the full potential of turbocharged vehicles.
Click on the following link to read another blog post: What is Bondo? Everything You Need to Know