What Is an O2 Sensor?
Learn the basics behind oxygen sensors, why they are important to your vehicle's performance, and how you can tell if yours needs replacing.
When you shop through retailer links on our site, we may earn affiliate commissions. Learn more
Ever pondered the secret behind the remarkable efficiency of today's modern automobiles? It may appear enigmatic, but the key lies in a small yet significant component: the O2 sensor. The O2 sensor is a linchpin in your vehicle's performance and efficiency, and comprehending its inner workings is crucial for ensuring the smooth and safe operation of your car.
We will embark on a journey to demystify the O2 sensor by exploring its nature, components, functions, and its paramount significance to car owners. Whether you're a newcomer to the world of auto mechanics or an experienced enthusiast, this post promises to enrich your understanding of your vehicle's distinct requirements!
IN THIS ARTICLE
What Is an O2 Sensor and How Does It Work?The Significance of O2 Sensors in Vehicle Performance
O2 Sensor Maintenance and Replacement
FAQs
What Is an O2 Sensor and How Does It Work?
The O2 sensor, commonly known as an oxygen sensor, is a pivotal component present in contemporary automobiles. It plays a pivotal role in overseeing and regulating the air-fuel mixture within the engine. Sometimes called a lambda sensor, it serves as an integral part of the emissions control system. Let's explore its functioning and purpose:
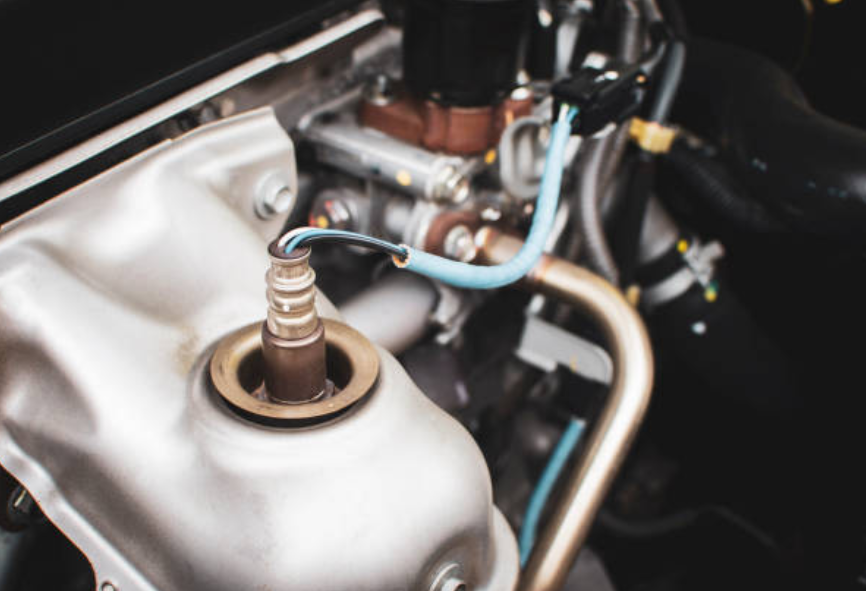
Depending on the architecture of the car, oxygen sensors are often installed either before or after the catalytic converter in the exhaust system. The most popular kind of O2 sensor is the zirconia sensor, which works by utilizing an oxygen ion chemical reaction.

Related Articles
The Significance of O2 Sensors in Vehicle Performance
The core role of an O2 sensor is to gauge the oxygen content within the exhaust gases as they exit the engine. This data is subsequently employed by the engine control unit (ECU) to fine-tune the air-fuel mixture, aiming for an ideal combustion. This ideal involves maintaining a specific air-fuel ratio, typically around 14.7 parts of air to 1 part of fuel (14.7:1), a state known as stoichiometric. This precise ratio is key to efficient combustion and the minimization of detrimental emissions.
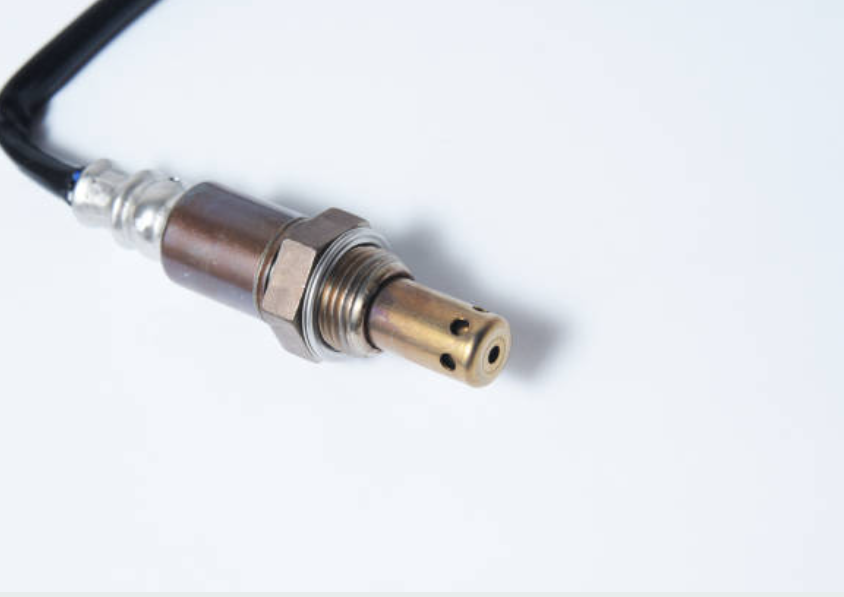

O2 Sensor Maintenance and Replacement
Maintaining and replacing O2 sensors is a critical aspect of vehicle upkeep. Regular inspection, which includes checking for physical damage and clean electrical connections, can help identify early issues. Cleaning the sensor tip is a temporary solution for contamination-related problems. Addressing engine problems like misfires, oil leaks, or coolant leaks promptly can prevent further sensor damage.
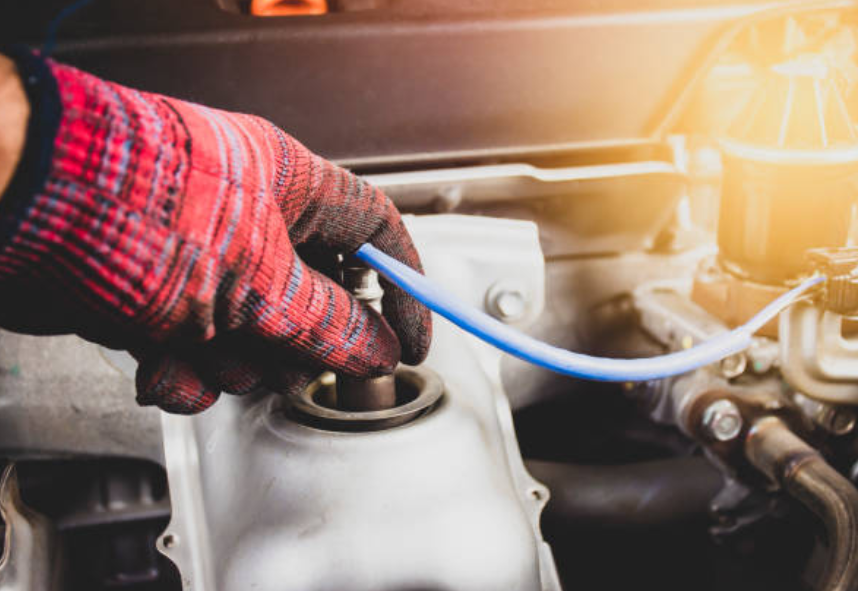

When it comes to replacement, it's crucial to diagnose the specific faulty sensor, either through a diagnostic code reader or with the help of a professional mechanic. Selecting the right replacement sensor is equally important, as different vehicles may require different types and designs of O2 sensors. Safety precautions, including disconnecting the battery, must be observed.
The old sensor should be removed carefully, and the new one installed according to manufacturer torque specifications. Reconnecting the wiring and resetting the Engine Control Unit (ECU) are the final steps to ensure a successful replacement. Proper maintenance and timely sensor replacement contribute to improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and overall vehicle performance, making them essential practices for responsible vehicle ownership.
FAQs
-
Can I replace an O2 sensor myself?
O2 sensor replacement is a task that some DIY enthusiasts can tackle, but it depends on your level of automotive expertise and the specific vehicle. If you're unsure, it's advisable to have a professional mechanic perform the replacement.
-
Can a faulty O2 sensor damage the engine?
A malfunctioning O2 sensor can indirectly cause engine damage if it leads to an excessively rich or lean air-fuel mixture. Over time, this may result in issues like fouled spark plugs, damage to the catalytic converter, or reduced engine longevity.
See another review here: The 10 Best WiFi Backup Cameras For Stress-Free Parking