Everything You Need to Know About Intake Manifold Gaskets
Get the full scoop on intake manifold gaskets, what they do and why their replacement is important for your vehicle's performance. Learn more with Car And Truck!
When you shop through retailer links on our site, we may earn affiliate commissions. Learn more
There are numerous crucial components of your automobile that require maintenance when it comes to upkeep. One such component is the intake manifold gasket, which enables air and fuel to enter the cylinders to support engine operation. Not only do these gaskets play an essential role in helping with combustion, but they also help reduce exhaust gas leaks from occurring. Knowing when it’s time for intake manifold gasket replacement can mean the difference between a running car and one that won’t start. In this blog post, we'll discuss everything you need to know about intake manifold gaskets—from their purpose and function all the way down to symptom signs of failure as well as how best to address them!
IN THIS ARTICLE
What is an Intake Manifold Gasket?Why Intake Manifold Gasket Replacement is Important
Symptoms of a Faulty Intake Manifold Gasket
Preventative Measures for Intake Manifold Gaskets
FAQs
What is an Intake Manifold Gasket?
An intake manifold gasket is a sealing component situated between the intake manifold and the cylinder head of an internal combustion engine. Its primary function is to create an airtight seal between these two engine components. This seal ensures that the air-fuel mixture from the carburetor or fuel injection system reaches the combustion chambers without any leaks.
Crafted from robust materials capable of enduring the elevated temperatures, pressures, and vibrations prevalent within the engine compartment, intake manifold gaskets assume a substantial responsibility in upholding the structural soundness of the engine's air and fuel systems. This, in turn, leads to seamless operational performance, enhanced fuel efficiency, and effective control over emissions.

Related Articles
Why Intake Manifold Gasket Replacement is Important
Intake manifold gasket replacement is a critical procedure that significantly impacts the performance and durability of a vehicle's engine. This replacement is crucial for ensuring an airtight seal between the intake manifold and the cylinder head, preventing air leaks that could disrupt the proper air-fuel mixture ratio.
A compromised gasket can lead to reduced engine efficiency, decreased power output, and poor fuel economy. Also possible outcomes of a bad gasket are coolant leakage, engine overheating, and higher emissions. Drivers may enhance fuel economy, extend the life of the engine, and restore ideal combustion by replacing a worn or broken intake manifold gasket, making for a safer, smoother, and more dependable driving experience.
Symptoms of a Faulty Intake Manifold Gasket
Poor Engine Performance: A failing gasket can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to rough idling, hesitation during acceleration, and reduced overall engine performance.
Engine Misfires: Air leaks caused by a faulty gasket can result in incomplete combustion cycles, causing engine misfires and potentially damaging the catalytic converter.
Coolant Leaks: If the gasket fails near coolant passages, coolant can leak into the cylinders, leading to white smoke from the exhaust, overheating, and potential engine damage.
Low Coolant Levels: The radiator and reservoir may have low coolant levels as a result of a faulty gasket causing fluid to seep externally.
Excessive Fuel Consumption: Leaks in the air-fuel mixture may result in greater fuel consumption and decreased fuel efficiency.
Check Engine Light: A malfunctioning gasket can trigger the check engine light due to fluctuations in air-fuel ratios or emissions-related issues.
Oil Contamination: Leaky gaskets can allow oil to mix with the coolant or air-fuel mixture, leading to oil contamination and potentially damaging internal components.
Engine Overheating: Coolant leaks caused by a faulty gasket can lead to engine overheating, resulting in potential engine damage if not addressed promptly.
Unusual Smells: Coolant or oil leaks caused by a failing gasket can produce unusual smells, often described as a sweet or burnt odor, from the engine or exhaust.
Visible Coolant or Oil Leaks: Physical signs of coolant or oil leaks around the intake manifold area are indicators of a potential gasket issue.
Reduced Acceleration: A compromised gasket can affect the engine's responsiveness, resulting in slower acceleration and decreased power.
Rough Idling: Air leaks can disrupt the engine's smooth operation, leading to irregular idling or even stalling.
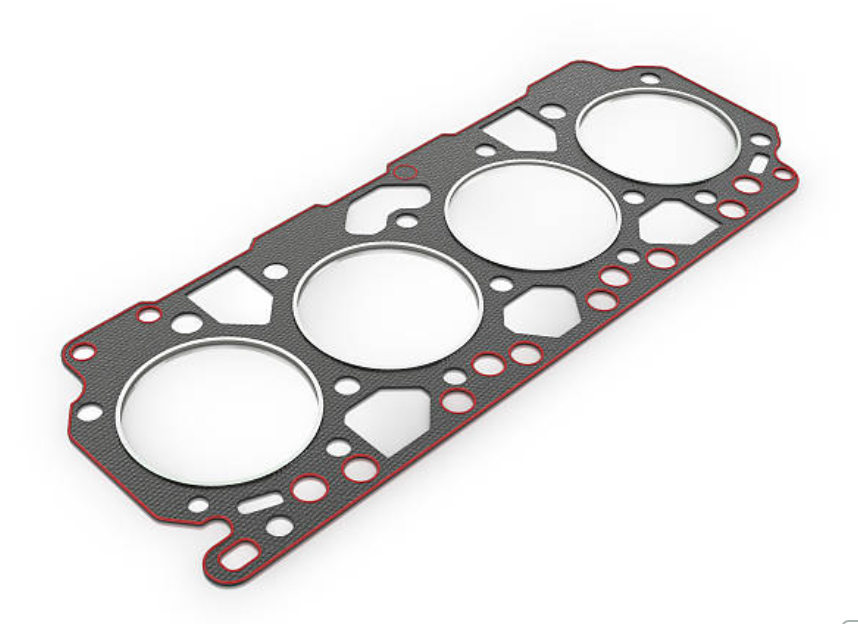

Preventative Measures for Intake Manifold Gaskets
Regular Maintenance: Adhere to your vehicle's recommended maintenance schedule. Regular maintenance can identify potential issues early and prevent gasket problems from escalating.
Cooling System Care: Maintain proper coolant levels and ensure the cooling system is functioning effectively. Overheating can stress the gasket and lead to premature failure.
Use Quality Parts: When replacing the intake manifold gasket or any related components, opt for high-quality parts from reputable manufacturers. Quality parts are more durable and less likely to fail.
Proper Torque Settings: During installation, follow the manufacturer's recommended torque settings for the intake manifold bolts. Over-tightening can damage the gasket, while under-tightening can lead to leaks.
Avoid Overheating: Avoid extended periods of engine overheating, as high temperatures can accelerate gasket deterioration.
Regular Inspections: Include the intake manifold gasket in your regular vehicle inspections. A professional mechanic can detect early signs of gasket wear or damage.
Address Leaks Promptly: If you notice coolant or oil leaks around the intake manifold area, address them promptly to prevent gasket damage.
Proper Fuel Quality: Using good-quality fuel can reduce the likelihood of carbon buildup in the engine, which can indirectly affect the gasket's performance.
Air Filter Maintenance: A clean air filter ensures proper airflow into the engine, helping maintain optimal combustion conditions and reducing stress on the gasket.
Professional Installations: When replacing the gasket, have the work done by experienced mechanics who follow proper installation procedures.
Avoid Over-Revving: Avoid excessive engine revving, especially when the engine is cold. This can prevent unnecessary stress on the gasket.
Monitor Engine Temperatures: Keep an eye on your engine's temperature gauge, and if you notice it consistently running hotter than normal, investigate and address the issue promptly.
FAQs
-
Do I need to replace other components when replacing the gasket?
Depending on the situation, it might be recommended to replace related components, such as the intake manifold bolts or associated seals, to ensure a complete and reliable repair.
-
Can a faulty intake manifold gasket affect emissions?
Yes, a faulty gasket can disrupt the air-fuel mixture and lead to incomplete combustion, potentially affecting emissions and triggering the check engine light.
See more review here: The 10 Best Running Watches For Fitness Enthusiasts